Today we’ll talk about a significant piece of legislation that’s making waves in Indiana—the Indiana Consumer Data Protection Act (ICDPA).
As a business owner, it’s crucial to get a grip on new laws, and this one is a biggie if your operations touch any data about people in Indiana.
This act focuses on providing transparency and safeguarding consumer privacy by outlining clear rules for data handling by businesses.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Is the ICDPA?
Passed in May 2023, the ICDPA is set to protect the privacy of consumers by ensuring they have control over their personal information. The law focuses on transparency and aims to make businesses more accountable for how they handle personal data.
It sets a framework for the ethical processing of personal information, encouraging businesses to adopt privacy-centric practices that respect consumer rights.
For more info on tools that can help safeguard your personal data in line with such regulations, you can check out Surfshark’s offerings for Windows. This resource can be particularly useful for understanding how technological solutions can assist in compliance with privacy laws.
When Does It Come Into Effect?
Mark your calendars for January 1, 2026. Although it seems like a while away, understanding and preparing for these changes now will make the transition much smoother. Starting early allows businesses ample time to adjust their processes and ensure full compliance by the deadline, avoiding any potential penalties.
Why Was It Enacted?
The ICDPA was created to safeguard individuals from the relentless onslaught of privacy issues and to provide them with substantial control over their personal data. It recognizes the right of consumers to know how their data is used and gives them power to dictate its usage.
Who Needs to Comply?
On May 1, 2023, Indiana enacted the data privacy legislation with the Indiana Consumer Data Protection Act (INCDPA), effective Jan. 1, 2026. Learn about its key provisions and how to ensure compliance.
Read more: https://t.co/frluApabCx#Indiana #INCDPA #PrivacyLaw #GetTerms
— GetTerms.io (@GetTermsIO) August 2, 2024
The law specifically targets for-profit entities that operate within Indiana or those that engage with Indiana residents, regardless of where the business itself is physically located.
To determine if your business falls under the jurisdiction of the ICDPA, you need to consider two main criteria related to the scale of your data processing activities:
Does your business handle personal data concerning more than 100,000 consumers annually?
Does your business process the personal data of at least 25,000 consumers and generate more than 50% of its annual revenue from the sale of this data?
If your business meets either of these conditions, it is subject to the ICDPA. This means that you may need to conduct a thorough review and potentially overhaul your data handling and processing practices.
The objective here is not merely to comply with the new regulations but also to ensure that consumer data is managed in a transparent and secure manner, respecting the privacy rights granted under the law.
Are There Exemptions?
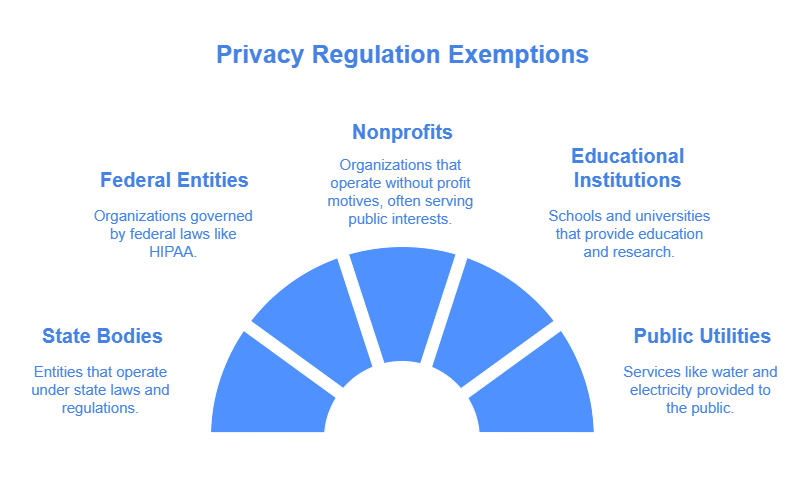
Not every entity needs to worry about the ICDPA. Exemptions include:
- State bodies and their affiliates
- Entities under federal regulations like the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act or HIPAA
Nonprofits, educational institutions, and public utilities These exemptions are provided to prevent overlap with existing privacy regulations that already cover these entities, ensuring that regulations are applied efficiently without redundancy.
Key Definitions to Know
When discussing the Indiana Consumer Data Protection Act (ICDPA), it’s crucial to start with the basics—what we mean by “Personal Data” and “Sensitive Data.”
Personal data refers to any information that can be used to identify an individual, whether directly or indirectly. This includes names, addresses, and even digital identifiers. However, it does not include information that has been anonymized, data that is publicly available, or aggregated data sets that cannot be traced back to any individual.
Sensitive data, on the other hand, encompasses information that reveals deeper aspects of an individual, such as racial or ethnic origins, religious beliefs, health status, and sexual orientation.
Responsibilities for Businesses
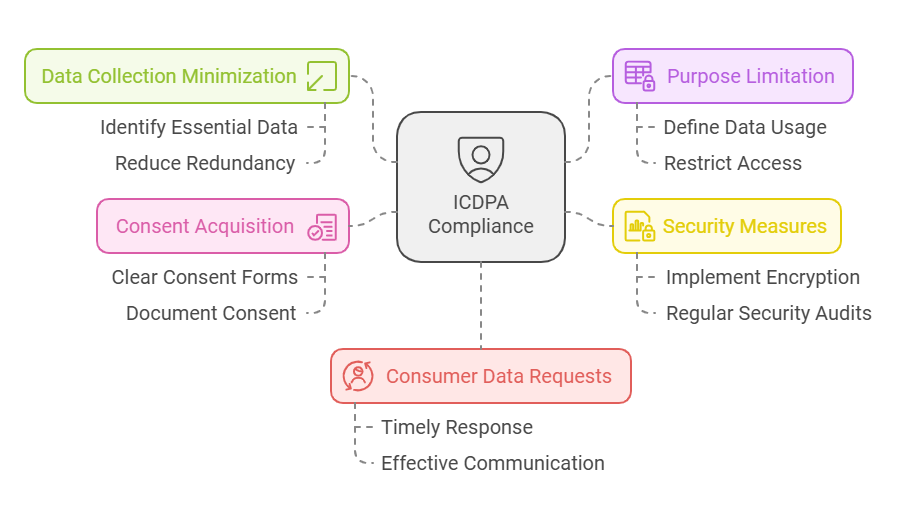
For businesses that fall within the scope of the ICDPA, a set of clear responsibilities must be followed to align with the law’s requirements.
- Minimize data collection to what’s necessary.
- Restrict data use to its original purpose.
- Implement strong security measures.
- Obtain explicit consent for processing sensitive data.
Handle consumer data requests swiftly and effectively.
These responsibilities emphasize respect for consumer privacy and aim to prevent the misuse of personal data, ensuring that it is handled with the utmost care.
Privacy Notice Must-Haves
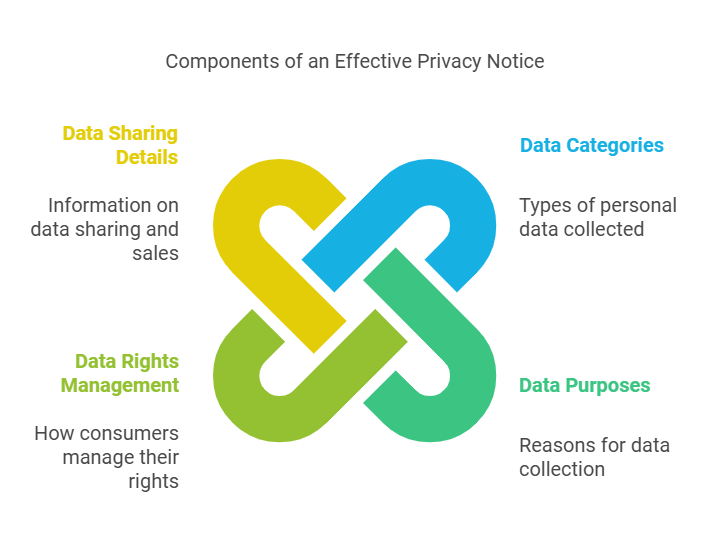
An effective privacy notice is an indispensable tool for compliance and transparency under the ICDPA. Your privacy notices should clearly articulate:
- The categories of personal data you collect.
- The purposes for which the data is collected.
- How consumers can manage their data rights.
Details about data sharing and sales, if applicable. Providing this information in a clear and accessible manner not only complies with the ICDPA but also enhances transparency, building stronger relationships with consumers.
Consumer Rights Under ICDPA
Consumers gain several key rights, including the ability to:
- Confirm if their data is being processed.
- Access and correct their data.
- Request deletion of their data.
Opt out of data sales or targeted advertising. These rights empower consumers to take control of their personal data, giving them the tools to protect their privacy proactively.
Enforcement and Penalties
[RFBT] Data Privacy Act: Definition of Terms
Source: IRRIRR: https://t.co/QwoAjQUVbD pic.twitter.com/AEzzbVjQ2Y
— lanz, CPA 2024 (@trialbalanz) October 29, 2024
The Indiana Attorney General has exclusive rights to enforce this law. Non-compliance can lead to injunctions and civil penalties up to $7,500 per incident. However, businesses get a 30-day grace period to address any issues before penalties kick in.
Steps Towards Compliance
For businesses gearing up for the ICDPA, the path to compliance involves several proactive steps. Updating privacy notices to reflect the new requirements is a starting point.
Conducting thorough data protection impact assessments is another critical step, as these assessments help businesses understand the impact of their data processing activities and identify necessary changes to enhance data protection.
Moreover, setting up accessible channels for consumer requests is essential. This not only helps in complying with the law but also positions the business as a consumer-friendly entity that values and respects consumer rights.
*These measures, collectively, do not just ensure compliance; they enhance a business’s reputation and trustworthiness in the eyes of consumers.
Closing Thoughts
Embracing the ICDPA is about respecting consumer privacy and enhancing the trust your customers place in your business. Start preparing now to ensure you’re ready when the law takes effect.
Related Posts:
- Lafayette, Indiana Population Statistics 2025 -…
- Indiana Lung Cancer Statistics 2025: Key Data and Trends
- How Indiana Became a Magnet for Data Center Projects in 2025
- Gary, Indiana Population in 2025 - Latest Census…
- How to Use Reliable Data Sources for Climate and…
- Is Indiana a Republican or Democratic State? True…









